Networking Basics - Certifications - Windows 7 - Windows 8 - Home Network Setup - Wireless Setup :: About - Contact - Search
IP v4 Tutorial
What is a class A IP v4 Address?
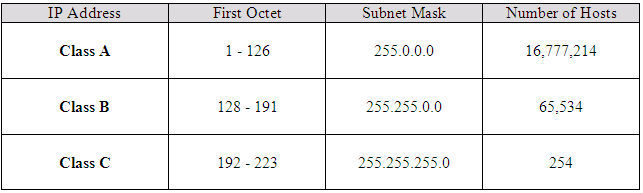
A class A address has a default subnet mask of 255.0.0.0.
Each octet can contain 256 possible values. This means a class A address supports 16,777,216 hosts on the network (256 x 256 x 256).
There are always two addresses that are reserved and can’t be used on a network. These two addresses are 10.0.0.0 and 10.255.255.255 The address of 10.255.255.255 is called the broadcast address and the 10.0.0.0 is the network address of a class A.
To identify a class A address you look at the first octet. The first octet always falls between the numbers 1 and 126. An address that starts with 127 is not allowed to be used because it is reserved for the loopback address. A few examples of a class A IP Address are:
15.23.85.2
95.87.12.4
120.32.45.5
The first octets of each of these IP Addresses are all between the class A range of 1 – 126.
What is a class B IP v4 Address?
A class B address has a default subnet mask of 255.255.0.0. This means that the first two octets are the network ID and the last two octets are host ID.
Class B addresses have an IP address in which the value of the first octet is between 128 and 191.
A class B address supports 65,536 hosts on the network. Don’t forget the two addresses that can’t be used. So this means you really have 65,534 addresses that can be assigned to hosts on the network.
Just remember that you can identify a class B address if the first octet is in the range of 128 – 191.
Examples of class B addresses:
130.123.5.4
156.35.24.2
190.23.57.86
What is a class C IP v4 ddress?
A class C address has a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. This means that the first three octets are the network ID and the last octet is the host ID.
A class C address can only support 254 hosts. (256 – 2)
A class C address can be identified when the first octet is between 192 and 223.
Examples of class C addesses:
192.168.1.3
196.86.23.4
203.23.86.7
What is a class D IP v4 address?
Class D addresses are used for special types of applications on the network known as multicasting applications. Applications will send data to the multicast address at the same time, and anyone who has registered with that address will receive the data.
A class D address can be identified when the first octet is between 224 and 239.
What is a class E v4 address?
This type of address was created for experimental purposes only. A class E address is rare on any network. The range of the first octet of a class E address is between 240 and 247.
Use this online calculator to understand IP Addresses and even subnetting.
To summarize the IP address tutorial:
There are 3 classes used on private networks.
Class A which the first octet ranges from 1 - 126 and uses a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0
Class B which the first octet ranges from 129 - 191 and uses a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0
Class C which the first octet ranges from 192 - 223 and uses a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0
Class D are used for multicasting
Class E is used for experimental purposes and is rarely used in today's networks.
In a private network like your home network an IP address must be unique in order to communicate. You can use which ever class for your network as long as every device has a unique IP. If you use DHCP then it will make sure that no IP address conflicts occur.
For each class, there are two IP addresses that are not used in every network, that is the network address and the private address.
For class A the network address is: 10.0.0.0 and broadcast address is 10.255.255.255 if using this IP scheme.
If you wanted to use something like 20.0.0. then the network address would be 20.0.0.0 and broadcast address would be 20.255.255.0.
Another example would be if you use a class C IP scheme, the network address would be 192.168.1.0 and broadcast address would be 192.168.1.255.
Go back to What is an IP Address or continue to What is a Firewall?
Return from IP v4 to Computer Networking Basics
Return from IP v4 to homepage of Computer Networking Success
"Didn't find what you were looking for? Use this search feature to find it."

1













New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave a comment in the box below.