Networking Basics - Certifications - Windows 7 - Windows 8 - Home Network Setup - Wireless Setup :: About - Contact - Search
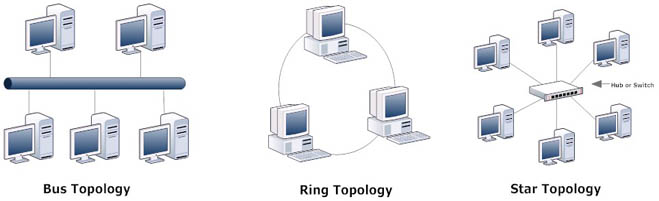
Network Topologies
What is a network topology?
Network topology refers to the shape of the network. Network topologies refer to how all the nodes (network devices) are wired together.
When you are planning a network, an important decision is the type of computer network topology you will implement.
Three main network topologies that shape it up!
When planning a network, there are 3 topologies to choose from that are in use today.
- Bus
- Ring
- Star
A Christmas-like Bus…
The bus is the simplest type of computer network topology but it has its drawbacks. This is a network that uses a single network cable from one end of the network to the other. The network devices are connected in line.
Think of how Christmas lights function. If one light goes out then the whole line of lights shut down.
The bus topology works the same way. If the network cable breaks anywhere, then the whole network is down….Ouch! Try to explain to your boss that you will spend the rest of the day troubleshooting the 100 workstations in the office until you find which connection is bringing the network down!
For this reason only older networks use this type of topology. It is the least expensive out of all the network topologies because you use less cable but it is not fun to manage.
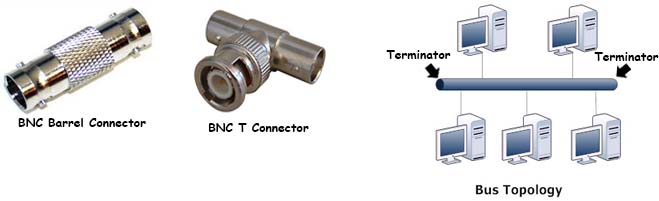
The bus computer network topology uses coaxial cable. Each end of each segment of the network has a special cable terminator on it. If this terminator is not present then the network will not function.
There are some bus topology networks that use Thin Ethernet (10Base-2). These types of networks use BNC connectors to tie all the cables together. Each computer uses a BNC T-connector which allows the computer to connect to the network and continue the bus.
Ring Topology
A ring topology refers more to the logical part of the network rather than physical. This means the network does not look like an actual ring when it is physically installed. Logically, there is an electrical “token” that circulates around the network like a ring.
For this reason, this type of computer network topology is called a token-ring.
The ring topology can look like a star topology but act as a ring topology. No other network topologies can accomplish this.
If a computer wants to transmit in this type of network, it waits until it has possession of the token. If an error changes the token pattern, then it can cause the token to stop circulating. The token-ring topology uses a central hub which can manage the circulation of the token.
So if you don’t have that token in possession then you can’t talk…you have to wait your turn.
Star topology
Out of all the network topologies the Star topology is the most commonly used in today’s LANs.
In this computer network topology, all the networking devices connect to a central hub or switch. This type of network uses Ethernet instead of token-ring.
(Your will learn about the Ethernet networking protocol in the next section….)
What is a Hub?
A hub is a device that is used in a wired network to connect Ethernet cables from network devices together. The hub allows each device to talk to one another. A hub is a multiport repeater. The disadvantage to a hub is that communication is slower than a switch. Let’s say the hub has 10 ports that allow 10 computers to connect to it. If computer on port 1 wants to talk to computer on port 10, then ports 2 – 9 will see the data because it is broadcasted to all ports. In a switch, port 1 can communicate directly with port 10 and this increases the speed of the network.
A hub looks like this.......

A hub and a switch look very similar in their appearance. To distinguish them you would have to read the label on its cover telling you it’s a hub or switch.
What is a switch?
A switch is a network device used to connect a number of devices together using Ethernet cables. The switch allows each device to talk with each other. A switch is faster than a hub and can allow direct communication from one computer to another. There are many advance configurations that make a switch a “smarter” device than a hub.
Here’s an example of a Switch
Let’s get back to the star topology.
The advantage to the star topology is that if one connection is broken, the rest of the network can still communicate with each other. The disadvantage is that it has one central point of failure. If the hub or switch breaks, then the whole network breaks.
All network devices have a hardware or physical address. They all have an IP address also remember?
Unlike an IP address, which can be changed by the administrator, in this case You….the physical address is “burned-in” to the actual network device. This physical address is called a MAC address.
A MAC address is 6 bytes or 48 bits in length. (1 byte = 8 bits)
Example of a MAC address: 00-FF-98-8C-58-86
The first 6 values are used to identify the vendor of the network device. The last 6 values are unique numbers assigned by the vendor. No MAC address in the world is duplicated. It is like your Social Security Number.
00-FF-98 = (identifies the vendor)
8C-58-86 = (uniquely assigned by the vendor)
A switch stores the hardware or physical address for each device that connect to its ports. When the switch stores these addresses, it can connect two nodes directly together without the need of broadcasting to every other port.
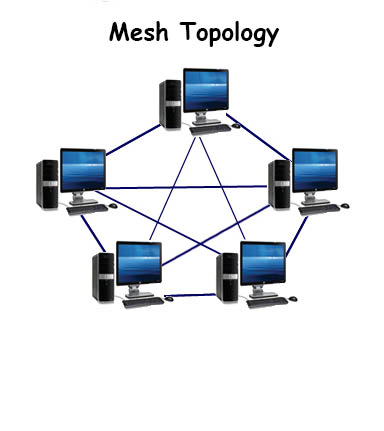
Bonus Topology…What a Mesh!
One last topology worth mentioning is called a mesh topology. This type of computer network topology is expensive because it requires all network devices to be wired to each other. This provides redundancy in the network data but it is too expensive to implement. It looks like a mess…I mean mesh!
<---Go back a section to "Computer LAN Network" or click next to "What is the Internet?" next --->
Return from Network Topologies to Computer Networking Basics
Return from Network Topologies to homepage of Computer Networking Success
"Didn't find what you were looking for? Use this search feature to find it."

1













New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave a comment in the box below.